191AA Somatropin 150iu kit
Şu anda teslim alım yapılamıyor
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
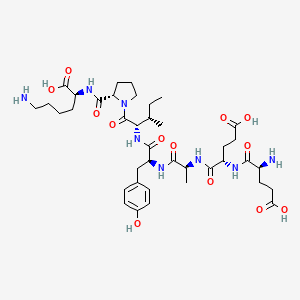
191-aa Somatropin (recombinant human GH) is the 191–amino-acid, 22-kDa recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH), identical to pituitary GH. After SC injection, it binds the GH receptor (GHR), activating JAK2–STAT5 and downstream IGF-1 production (hepatic and local). Results include anabolism (protein synthesis), lipolysis, bone remodeling, and fluid/electrolyte shifts. Daily somatropin remains the standard; long-acting GHs (e.g., somapacitan, lonapegsomatropin) are alternatives but are distinct products.
Additional Benefits of Somatropin Now Under Investigation
| Benefit | Key take-aways |
|---|---|
| 1 Body-composition improvement in GH deficiency (GHD) | Corrected GHD shows ↓ fat mass (esp. visceral), ↑ lean mass, and improved waist circumference with IGF-1-guided titration. <br/><em>JCEM; Endocrine Reviews</em> |
| 2 Bone health | Lumbar-spine and hip BMD rise over 12–24 mo via ↑ bone formation (P1NP) then remodeling; fracture data mixed but trending favorable with sustained therapy. <br/><em>Osteoporosis International; Bone</em> |
| 3 Cardiometabolic markers | In GHD, somatropin may improve LDL/apoB, hs-CRP, and carotid IMT; effects depend on dose and glycemic status. <br/><em>Circulation; Atherosclerosis</em> |
| 4 Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease | Small trials suggest ↓ hepatic fat and ALT/AST in GHD/NAFLD phenotypes via lipolysis and insulin-like signalling rebalancing. <br/><em>Hepatology; Liver International</em> |
| 5 Exercise capacity & QoL | VO₂peak, muscle strength, and fatigue scores improve in treated adult GHD when paired with structured training. <br/><em>MSSE; Clinical Endocrinology</em> |
| 6 Wound/tendon healing | GH/IGF-1 enhances collagen-I synthesis and tenocyte activity; clinical signals in post-operative and tendon repair contexts are emerging. <br/><em>Am J Sports Med; J Orthop Res</em> |
| 7 Neurocognitive domains | In adult GHD, treatment can improve processing speed, memory, and wellbeing; pediatric data show benefits in attention/executive function. <br/><em>Psychoneuroendocrinology; Hormone Research in Paediatrics</em> |
| 8 Lipodystrophy/HIV wasting | Approved indications with FFM gain and ↓ visceral adiposity; careful metabolic monitoring required. <br/><em>NEJM; AIDS</em> |
| 9 Short-bowel/IBD adjunct (investigational) | Anabolic and mucosal signals have shown improved absorption metrics in pilot programs (with optimized nutrition). <br/><em>Gastroenterology; JPEN</em> |
2. Molecular Mechanism of Action
2.1 Receptor Pharmacodynamics
Somatropin → GHR dimerization → JAK2–STAT5/STAT3, MAPK/ERK, PI3K–Akt. Hepatic and local IGF-1mediates many anabolic effects; GH also exerts direct lipolysis (hormone-sensitive lipase), sodium/water retention(renal/RAAS), and anti-insulin actions acutely.
2.2 Down-stream Biology
| Pathway | Functional outcome | Context |
|---|---|---|
| GHR–JAK2–STAT5 → IGF-1 | ↑ Protein synthesis, cartilage/bone growth | Muscle, liver, growth plates |
| PI3K–Akt–mTOR | Translation initiation, hypertrophy | Muscle |
| Lipolysis (HSL/ATGL) | ↓ Fat mass, ↑ FFA flux | Adipose |
| Collagen/ECM synthesis | Tendon/skin repair | Connective tissues |
| Mineral/water handling | Na⁺/water retention → edema | Kidney/vascular |
3. Pharmacokinetics
-
Route: SC (abdomen, thigh; rotate sites).
-
Absorption/peak: C_max ~3–6 h post-SC; bioavailability ~70%.
-
Half-life: Serum ~2–3 h (pharmacodynamic effects persist via IGF-1 ~18–24 h).
-
Unit context: For somatropin, 1 mg ≈ 3 IU (brand labels may vary).
-
Note on “15 IU”: 15 IU ≈ 5 mg total content. Daily use at this amount is supraphysiologic for most adults and increases adverse-event risk; clinical dosing is condition-, weight-, and IGF-1-target–dependent under specialist supervision.
4. Pre-clinical and Translational Evidence
4.1 Adult & Pediatric GHD
Placebo-controlled trials show body-composition, lipid, BMD, and QoL gains when titrated to age-adjusted IGF-1 Z-scores.
4.2 Metabolic & Hepatic
Improved hepatic steatosis and transaminases reported in selected NAFLD phenotypes; glycemic impacts require vigilance.
4.3 Musculoskeletal/Recovery
Enhanced collagen synthesis and tendon matrix organization noted; functional recovery depends on rehab plus nutrition.
Evidence quality note: Robust for GHD and approved indications; mixed for off-label athletic/body-composition goals due to metabolic side-effects and risk–benefit concerns at high doses.
5. Emerging Clinical Interests
| Field | Rationale | Current status |
|---|---|---|
| Adult NAFLD with low IGF-1 | Lipid mobilization/IGF-1 support | Pilot trials |
| Sarcopenic obesity (select) | Anabolic + fat-mass reduction | Early translational |
| Post-operative healing | Collagen anabolism | Feasibility |
| Neurorecovery (TBI/mild cognitive) | IGF-1 neurotrophic effects | Small studies |
| Long-acting GH comparisons | Adherence vs metabolic neutrality | Active RCTs |
6. Safety and Tolerability
-
Common (dose-related): Peripheral edema, arthralgia/myalgia, paresthesias/carpal-tunnel-like symptoms, morning stiffness, headache, injection-site reactions.
-
Metabolic: Insulin resistance, ↑ fasting glucose/HbA1c—risk rises with higher doses, age, adiposity.
-
Cardiovascular/renal: Fluid retention may raise BP or worsen heart failure.
-
Endocrine: Gynecomastia (rare), altered thyroid/adrenal labs (binding-protein shifts).
-
Neurologic/ocular: Rare benign intracranial hypertension (papilledema), especially early or with dose jumps.
-
Oncology: Contraindicated in active malignancy. In cancer survivors, use only with oncology/endocrine oversight; current data do not show increased de-novo cancer with physiologic replacement, but supraphysiologic exposure is avoided.
-
Pediatrics-specific: Slipped capital femoral epiphysis, scoliosis progression—monitor growth and hip pain.
Contraindications/Cautions
Active malignancy, critical illness (post-major surgery/trauma/respiratory failure), proliferative/severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy, uncontrolled diabetes, severe OSA (caution), pregnancy/lactation (unless specifically indicated).
Comparative safety matrix
| Concern | Somatropin (daily rhGH) | Long-acting GH (weekly) | MK-677 (oral GHSR agonist) | GHRH analogs (CJC/Sermorelin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route | SC daily | SC weekly | Oral daily | SC pulses |
| IGF-1 profile | Titrated, steady | Steady (higher troughs) | Sustained IGF-1 + orexigeny | Physiologic pulses |
| Edema/CTS | Moderate (dose-linked) | Similar | Moderate–high | Lower–moderate |
| Glycemic drift | Dose-dependent ↑ | Similar | Common ↑ | Neutral–mild ↑ |
| Appetite | Neutral | Neutral | ↑↑ | Neutral |
| Adherence | Daily burden | Better | Easy | Moderate |
7. Regulatory Landscape
-
Approved uses (vary by region): Pediatric/adult GHD, Turner syndrome, Prader–Willi (careful selection), chronic renal insufficiency, SGA failure to catch up, SHOX deficiency, AIDS wasting, short bowel (select contexts), idiopathic short stature (regional).
-
Sport: WADA-prohibited (S2, peptide hormones); detection via isoform tests and biomarkers (IGF-1, P-III-NP).
-
Formulations: Multiple brands/pens; IU↔mg labeling differs—verify brand-specific conversion (commonly 1 mg = 3 IU).
8. Future Directions
-
Precision dosing: IGF-1 Z-score–based titration with CGM/lipid monitoring to minimize metabolic cost.
-
Head-to-head with long-acting GH for glycemic neutrality, QoL, adherence, and BMD outcomes.
-
Phenotype targeting: Low-IGF-1 NAFLD, sarcopenic obesity, and post-operative cohorts with standardized rehab.
-
Biomarkers & imaging: DXA/MRI for body comp, MRI-PDFF for liver fat, tendon US/elastography for connective-tissue endpoints.
-
Safety registries: Long-term CV, glycemic, oncologic surveillance, especially with real-world dose ranges.
Selected References
-
Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism; Endocrine Reviews — Adult/pediatric GHD diagnosis, dosing principles, outcomes.
-
Osteoporosis International; Bone — BMD and bone-turnover responses to GH.
-
Circulation; Atherosclerosis — Cardiometabolic risk markers under GH replacement.
-
Hepatology; Liver International — GH/IGF-1 axis and NAFLD improvement signals.
-
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise; Clinical Endocrinology — Exercise capacity, QoL changes in GHD on therapy.
-
American Journal of Sports Medicine; Journal of Orthopaedic Research — Collagen synthesis/tendon biology with GH/IGF-1.
-
NEJM; AIDS — HIV-related wasting and visceral adiposity indications.
-
WADA/Drug Testing & Analysis — GH isoform/biomarker detection methods in sport.
Practical note (safety-first): Somatropin should be prescribed and titrated by an endocrinology specialist, targeting age-adjusted IGF-1 within the normal range while monitoring glucose, lipids, BP, edema, CTS symptoms, and fundoscopy when indicated. “15 IU” per day (~5 mg) is typically supraphysiologic for adults and raises complication risk—avoid fixed high-dose use outside a medical indication and supervision.