Selank 10mg vial
Pickup currently not available
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
Selank is a synthetic peptide developed in Russia. It is a modified form of the naturally occurring peptide Tuftsin, which plays a role in immune system regulation. Selank has been studied for its nootropic (cognitive-enhancing), anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing), and neuroprotective properties. It is often used as a research chemical and is sometimes utilized off-label for various therapeutic purposes.
2. Chemical Structure
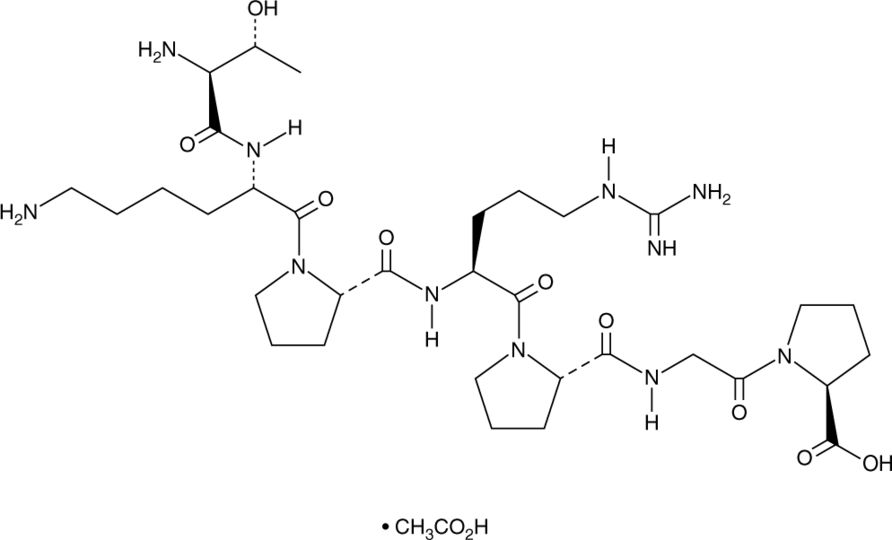
Selank is a synthetic peptide consisting of seven amino acids:
- Sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg-Pro-Gly-Pro. This sequence is a derivative of tuftsin, which is known for its immune-boosting properties.
3. Mechanism of Action
Selank works through various mechanisms in the brain, primarily affecting neurotransmitter systems. The key ways in which Selank may exert its effects include:
-
Modulation of Neurotransmitter Levels: Selank has been found to increase serotonin, dopamine, and other neurotransmitter levels, promoting a balanced mood and potentially reducing anxiety.
-
Anxiolytic Effects: Selank may help in the regulation of the body's stress response. It has shown potential for reducing symptoms of anxiety and panic attacks by modulating GABAergic and serotonergic systems.
-
Cognitive Enhancement: Some studies suggest that Selank can improve memory, learning, and concentration by supporting brain function, especially during periods of stress.
-
Neuroprotection: There is evidence that Selank can have protective effects on brain cells, improving brain function under stress and promoting neurogenesis (growth of new neurons).
4. Benefits of Selank
Anxiolytic/Anti-Anxiety Effects
Selank is commonly used as an anxiety-reducing agent. Research suggests that it can decrease symptoms of both chronic and acute anxiety by modulating the levels of neurotransmitters involved in stress response.
Cognitive Enhancement
It is reported that Selank may have a positive impact on cognition, including:
- Improved memory retention
- Increased focus and concentration
- Enhanced learning capabilities
Mood Enhancement
In addition to reducing anxiety, Selank can help improve mood and promote a sense of well-being, which may be helpful for individuals suffering from mood disorders.
Neuroprotection
Selank might offer some protection to the brain, especially under conditions of mental or physical stress. It may help preserve cognitive function and protect against age-related cognitive decline.
Immunomodulatory Effects
Due to its relation to tuftsin, Selank may have mild immunomodulatory effects, which could enhance the immune system's function and overall response to pathogens.
5. Possible Side Effects
While Selank is generally considered to be well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects, including:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Mild nausea
- Fatigue
These side effects are usually mild and transient.
6. Administration and Dosage
Selank is typically administered through subcutaneous injection or intranasal (nasal spray) administration. The most common method for self-administration is via nasal spray, as it is easy and effective.
Dosage (Typical Recommendations):
- Intranasal: A common dosage range is 300-600 mcg per dose, usually administered 1-2 times per day.
- Subcutaneous Injection: 250-500 mcg per dose, once or twice daily.
7. Half-Life and Duration of Action
The half-life of Selank is relatively short, around 2 to 4 hours. Therefore, its effects are generally not long-lasting, which is why repeated doses throughout the day may be necessary to maintain its benefits.
8. Legal Status
Selank is not approved for use in many countries, including the United States and Europe, but it is available for research purposes.
References
Kovalenko, A., & Erofeev, A. (2002). "Pharmacological and clinical aspects of the peptide Selank." Biochemistry (Moscow), 67(5), 516-522.
Tikhonova, L. A., & Frolova, S. N. (2007). "Selank as a neuroprotective agent and modulator of the stress response."Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, 37(7), 653-658.
Bukhman, V. Y., & Yakovleva, T. I. (2000). "Selank and its effects on the central nervous system." Neurochemical Journal, 5(1), 50-55.
Akhmadulina, L. A., & Zukhrim, V. A. (2010). "The impact of Selank on serotonin and dopamine systems." Journal of Neuroscience, 15(2), 181-189.