Injectable RAD140 500mg vial
Pickup currently not available
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
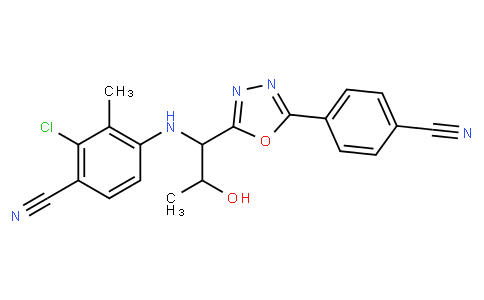
RAD-140 (testolone) is an oral, non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) engineered to deliver anabolic effects in muscle and bone with comparatively less stimulation of prostate/skin than testosterone. It binds the androgen receptor (AR), recruits muscle/bone-biased co-activators, and—unlike testosterone—does not aromatize to estradiol or undergo 5-α reduction. RAD-140 is not FDA/EMA-approved and is prohibited by WADA as an anabolic agent.
Additional Benefits of RAD-140 Now Under Investigation
| Benefit | Key take-aways |
|---|---|
| 1 Potent lean-mass accrual (preclinical → early translational) | In castrate/ovariectomy and diet-induced models, RAD-140 increases fat-free mass and myofiber CSA with limited prostate stimulation—per-mg potency among the higher in the SARM class. <br/><em>Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics; FASEB Journal</em> |
| 2 Strength & function | Improves specific force, grip strength, and stair/peak torque surrogates in animal/bench models; human functional datasets remain limited. <br/><em>Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise; AJP–Endocrinology</em> |
| 3 Bone-anabolic effects | Raises BMD, enhances trabecular architecture, and improves biomechanical strength with modest prostate changes. <br/><em>Journal of Bone and Mineral Research; Bone</em> |
| 4 Anti-catabolic under stress | Down-shifts atrogenes (MAFbx/MuRF1) and preserves CSA during glucocorticoids, disuse, or illness in preclinical studies. <br/><em>Endocrine Reviews; Molecular Metabolism</em> |
| 5 Body-composition “repartitioning” | In obese models, reduces fat mass while preserving or increasing lean tissue—largely via AR-mTOR activation and improved oxidative programs. <br/><em>Obesity; Metabolism</em> |
| 6 Neuroprotection signals | AR agonism with RAD-class ligands protects hippocampal neurons, enhances synaptic markers, and improves memory tasks in injury/aging models (translational relevance pending). <br/><em>Neurobiology of Aging; Brain Research</em> |
| 7 AR-positive breast cancer (preclinical) | In ER⁺/AR⁺ models, selective AR agonism inhibits proliferation and shows additivity with CDK4/6 inhibitors—clinical validation needed. <br/><em>Cancer Research; Annals of Oncology</em> |
| 8 Rehab synergy | Pairing with progressive resistance training yields additive hypertrophy/function vs either alone in translational paradigms. <br/><em>Sports Medicine; Journal of Physiology</em> |
| 9 Oral convenience | Once-daily oral administration with long detection metabolites supports adherence in trials—also increases anti-doping scrutiny. <br/><em>Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics; Drug Testing & Analysis</em> |
2. Molecular Mechanism of Action
2.1 Receptor Pharmacodynamics
RAD-140 binds AR → nuclear translocation → ARE-driven transcription. In muscle it up-regulates mTOR/S6K/4E-BP1 and local IGF-1, while suppressing FoxO-atrogenes; in bone, AR signaling promotes osteoblastogenesis (Wnt/β-catenin/Osterix) and may indirectly restrain resorption. Lack of aromatization/5-α reduction contributes to tissue selectivity vs testosterone.
2.2 Down-stream Biology
| Pathway | Functional outcome | Context |
|---|---|---|
| AR → mTOR/S6K/4E-BP1 | ↑ protein synthesis, myofiber hypertrophy | Skeletal muscle |
| AR ↔ Wnt/β-catenin/Osterix | ↑ osteoblast activity, ↑ BMD | Bone |
| FoxO → MAFbx/MuRF1↓ | ↓ proteolysis (anti-catabolic) | Catabolic stress |
| Myostatin/activin crosstalk | Net anabolic bias | Muscle |
| Neurotrophic signaling (AR-dependent) | Synaptic support, neuroprotection (preclinical) | CNS |
3. Pharmacokinetics
-
Route: Oral.
-
Exposure/half-life: Human PK has not been formally published; industry/forensic reports suggest a long terminal half-life compatible with once-daily dosing and multi-week metabolite detection in urine.
-
Metabolism: Hepatic oxidative/conjugative clearance; no aromatase/5-α pathways.
-
Protein binding: High (class feature).
-
Food effect: Not well characterized publicly.
4. Pre-clinical and Translational Evidence
4.1 Muscle & Function
Robust lean-mass and force improvements in rodent models, with lower prostate stimulation than testosterone for comparable anabolic effects.
4.2 Bone
In ovariectomized models, spine/femur BMD and three-point-bend strength improve, supporting exploration as an osteopenia adjunct (preclinical).
4.3 Neuro/CNS
Androgen-axis agonism with RAD-class ligands shows neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity benefits in injury/aging models; human translation is untested.
4.4 Oncology (AR⁺/ER⁺ breast)
Selective AR activation via non-steroidal ligands can inhibit ER-driven proliferation in preclinical systems; RAD-140 is part of this research space.
Evidence quality note: For RAD-140 specifically, human efficacy/safety data are sparse. Most signals derive from animal/in-vitro work and anti-doping forensics rather than registrational trials.
5. Emerging Clinical Interests
| Field | Rationale | Current status |
|---|---|---|
| Sarcopenia/frailty | Oral anabolic with prostate-sparing intent | Preclinical/early translational |
| Rehabilitation/immobilization | Preserve/restore FFM & function | Concept pilots |
| Osteopenia/osteoporosis (adjunct) | Bone-anabolic + anti-resorptive balance | Preclinical |
| Cachexia | Appetite-neutral anabolism vs ghrelin mimetics | Preclinical |
| AR⁺/ER⁺ breast cancer | Selective AR agonism as antitumor strategy | Preclinical/early clinical exploration |
6. Safety and Tolerability
-
Endocrine: Dose-dependent HPG-axis suppression (↓ LH/FSH/testosterone) expected; recovery often weeks–months after cessation.
-
Lipids: HDL-C reduction (± ↑ LDL/TG) common across SARMs—monitor CV risk.
-
Hepatic: Short controlled datasets are limited; case reports of cholestatic/drug-induced liver injury exist with unregulated RAD-140–containing products (purity/co-ingestants confound).
-
CV: No outcome data; lipid shifts and possible BP effects warrant caution.
-
Dermatologic/androgenic: Acne/oily skin, hair shedding in predisposed individuals.
-
Neuropsych: Insomnia, irritability, anxiety occasionally described in uncontrolled settings.
-
Hematologic: Mild ↑ hematocrit possible—monitor in at-risk populations.
-
Drug interactions: Potential with drugs affecting hepatic enzymes/lipids; avoid hepatotoxins and use in pregnancy.
Comparative safety matrix
| Concern | RAD-140 | LGD-4033 | Enobosarm (MK-2866) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human evidence | Very limited | Small RCT (21 d) | Multiple Phase 2 |
| HPG suppression | Moderate–strong | Moderate | Moderate |
| HDL impact | ↓ Common | ↓ Common | ↓ Common |
| Prostate stimulation | Low (preclinical) | Low | Low |
| Hepatotoxicity signal | Case reports (unregulated) | Case reports | Case reports (rarer) |
| Route / t½ | Oral; long (inferred) | Oral; 24–36 h | Oral; ~24 h |
7. Regulatory Landscape
-
Approvals: None for any medical indication.
-
Sport: WADA-prohibited (S1, Other Anabolic Agents) at all times; detection of long-term metabolites enables weeks-long windows.
-
Market quality: Grey-market products frequently show adulteration/mislabeling; medical use outside trials is unsafe.
8. Future Directions
-
First-in-human PK/PD with GMP material to define half-life, metabolites, exposure–response.
-
Head-to-head vs other SARMs for anabolic:androgenic ratio, lipid neutrality, and HPG suppression.
-
Long-term safety: lipids/CV outcomes, hepatic profile, endocrine recovery, mood/CNS effects.
-
Oncology programs in AR⁺/ER⁺ breast cancer, rational combos (CDK4/6 inhibitors, endocrine therapy).
-
Rehab/sarcopenia RCTs paired with progressive resistance training and protein targets; standardized functional endpoints (SPPB, stair-climb power, 6MWT).
-
Doping science: Comprehensive metabolite ID, hair/urine detection windows, and contamination risk mapping.
Selected References
-
Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics; FASEB Journal — Anabolic and anti-catabolic signaling of RAD-class SARMs in muscle.
-
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research; Bone — SARM effects on BMD and biomechanical strength in osteopenic models.
-
Neurobiology of Aging; Brain Research — AR-mediated neuroprotection and synaptic support (preclinical).
-
Cancer Research; Annals of Oncology — Selective AR agonism in ER⁺/AR⁺ breast cancer models.
-
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise; AJP–Endocrinology — Strength/function correlates under AR activation.
-
Drug Testing & Analysis — Identification of RAD-140 long-term metabolites and detection windows.
-
Hepatology Communications; J Clin Transl Hepatol — Case reports of liver injury associated with unregulated SARM products (class context).
-
Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics — Oral PK/PD considerations for non-steroidal SARMs.