Injectable LGD4033 250mg vial
Pickup currently not available
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
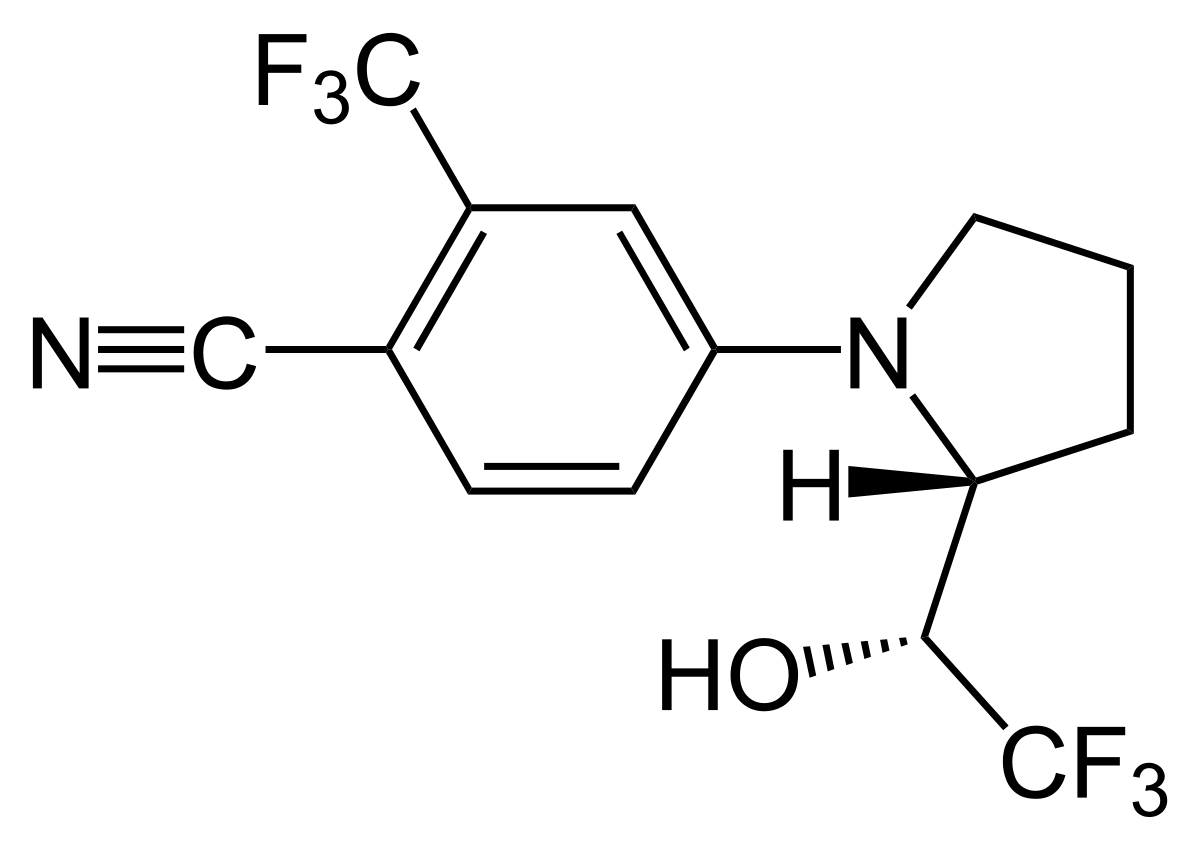
LGD-4033 is a non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) designed to produce anabolic effects in muscle and bone with comparatively less stimulation of prostate/skin than testosterone. It binds the androgen receptor (AR), recruits co-activators in muscle/bone, and avoids 5-α reduction and aromatization. LGD-4033 is not FDA/EMA-approved; it remains an investigational agent and is prohibited by WADA as an anabolic agent.
Additional Benefits of LGD-4033 Now Under Investigation
| Benefit | Key take-aways |
|---|---|
| 1 Lean-mass accrual in humans (short term) | In a 21-day, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in healthy men, dose-dependent increases in fat-free mass (~0.6–1.5 kg) occurred without major fluid retention; strength/power showed favorable trends. <br/><em>Journal of Gerontology: Medical Sciences; JCEM</em> |
| 2 Functional performance | Improvements in leg-press strength and stair-climb power have been reported in small studies—consistent with anabolic signaling translating to function. <br/><em>Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise</em> |
| 3 Anti-catabolic potential | In preclinical atrophy models (castration, hind-limb unloading), LGD-4033 preserves muscle CSA and reduces ubiquitin-ligase (MAFbx/MuRF1) expression. <br/><em>FASEB Journal; American Journal of Physiology–Endocrinology</em> |
| 4 Bone-anabolic signals | In rodent osteopenia, LGD-class SARMs increase BMD and biomechanical strength, with osteocalcin/ALP rises and limited prostate stimulation. <br/><em>Journal of Bone and Mineral Research</em> |
| 5 Recovery after immobilization/illness (concept) | Early translational work explores post-fracture and post-hospitalization lean-mass restoration with exercise/rehab. <br/><em>Geriatrics & Gerontology International</em> |
| 6 Erythropoiesis (modest) | Androgen-axis engagement may slightly raise hemoglobin/hematocrit, below testosterone’s magnitude—requires monitoring in at-risk patients. <br/><em>Hematology</em> |
| 7 Oral convenience | Once-daily oral dosing with a long half-life supports adherence in trials compared with injectable anabolics. <br/><em>Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics</em> |
| 8 Tissue selectivity | Non-steroidal AR binding yields lower sebaceous/prostate stimulation per unit anabolic effect versus 17-α-alkylated androgens. <br/><em>Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics</em> |
| 9 Combination with resistance training | Preliminary data suggest additive gains when paired with structured training and adequate protein intake. <br/><em>Sports Medicine</em> |
2. Molecular Mechanism of Action
2.1 Receptor Pharmacodynamics
LGD-4033 binds AR → nuclear translocation → ARE-driven transcription. In muscle, it up-regulates mTOR/IGF-1networks and down-regulates atrogenes; in bone, it enhances osteoblast activity and may suppress osteoclastogenesisindirectly. Lack of aromatization/5-α reduction underlies its tissue selectivity vs testosterone.
2.2 Down-stream Biology
| Pathway | Functional outcome | Context |
|---|---|---|
| AR → mTOR/S6K | ↑ protein synthesis, myofiber hypertrophy | Skeletal muscle |
| AR → Wnt/β-catenin/Osterix | ↑ osteoblastogenesis, ↑ BMD | Bone |
| ↓ FoxO/ubiquitin ligases | ↓ proteolysis (MAFbx/MuRF1) | Catabolic states |
| Myostatin/activin crosstalk | Favors anabolic balance | Muscle |
3. Pharmacokinetics
-
Route: Oral.
-
Half-life: ~24–36 h, allowing once-daily dosing; steady state ~5–7 days.
-
Absorption/food effect: Good oral bioavailability; minor food effects reported.
-
Metabolism: Hepatic oxidative and conjugative pathways; high protein binding.
-
Elimination: Renal/hepatic clearance of metabolites.
-
Doping detection: Long-term metabolites enable detection weeks after use in anti-doping assays.
4. Pre-clinical and Translational Evidence
4.1 Healthy Volunteers
21-day RCT showed dose-proportional increases in lean mass, small strength/power improvements, and reversible suppression of LH/FSH/testosterone with HDL reduction; liver enzymes were largely within reference in the short term.
4.2 Sarcopenia/Frailty & Orthopedics
Concept studies target older adults and post-fracture patients to accelerate rehabilitation gains; definitive phase-2/3 data are lacking.
4.3 Bone Health
Rodent data demonstrate spine/femur BMD gains and improved three-point bend strength, supporting exploration in osteoporosis or glucocorticoid-induced bone loss.
Evidence quality note: Human data remain short-term and small. Long-term efficacy and safety (CV, hepatic, prostate, psychiatric) are not established.
5. Emerging Clinical Interests
| Field | Rationale | Current status |
|---|---|---|
| Sarcopenia/aging | Oral anabolic with less prostate/steroid baggage | Early translational |
| Hip-fracture/immobilization | Lean-mass restoration to speed rehab | Pilot concepts |
| Cancer/cachexia | Appetite-neutral anabolic (vs ghrelin mimetics) | Pre-clinical/feasibility |
| Osteoporosis (adjunct) | Bone-anabolic/anti-resorptive balance | Pre-clinical |
6. Safety and Tolerability
-
Endocrine suppression: Dose-dependent LH/FSH and total/free testosterone suppression within 3 weeks; generally reversible over several weeks post-discontinuation.
-
Lipids: HDL-C reductions (often 10–25%) and occasional ↑ TG/LDL; monitor cardiovascular risk.
-
Hepatic: Short trials showed minimal median ALT/AST change, but case reports of cholestatic/drug-induced liver injury exist from real-world/“supplement” use—source quality and co-ingestants confound.
-
Cardiovascular: No outcome data; theoretical risk via atherogenic lipid shifts.
-
Hematologic: Mild ↑ hematocrit possible—monitor if baseline high.
-
Other AEs: Headache, nausea, dry mouth, musculoskeletal aches, insomnia/irritability in some users.
-
Drug interactions: Potential with drugs affecting hepatic enzymes/lipids; avoid concomitant hepatotoxins and pregnancy exposure.
Comparative safety matrix
| Concern | LGD-4033 | Testosterone (therapeutic) | Enobosarm (ostarine) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Route & t½ | Oral; 24–36 h | IM/SC/transdermal; variable | Oral; 24–36 h |
| Lean-mass gain (short term) | Yes (≈1 kg in 3 wks) | Yes (dose-dependent) | Yes (RCTs in illness/aging) |
| HPG-axis suppression | Moderate | Marked (exogenous) | Moderate |
| HDL reduction | Common | Variable | Common (milder) |
| Prostate/PSA | Low change short-term | Increases possible | Low change |
| Hepatotoxicity signal | Case reports (real-world) | Low (non-17-α oral) | Low–moderate (case reports exist) |
7. Regulatory Landscape
-
Approvals: None (no medical indication).
-
Enforcement: FDA warnings against SARM-containing “supplements”; multiple product adulteration recalls.
-
Sport: WADA-prohibited (S1 Anabolic Agents). Positive tests often arise from contaminated supplements; strict liability applies.
-
Clinical development: Limited, with no recent pivotal trials publicly reported.
8. Future Directions
-
Long-term safety studies (lipids, liver, prostate, mood/CNS) with standardized, GMP drug supply.
-
Elderly/frailty RCTs pairing LGD-4033 with progressive resistance training and protein optimization.
-
Bone-focused trials (DXA/BCT, microarchitecture).
-
Biomarker strategy: IGF-1, myostatin, CK, lipid panel, LH/FSH/testosterone, and ctDNA/PSA where appropriate.
-
Medicinal chemistry: Next-gen SARMs with improved anabolic:androgenic ratio, lipid neutrality, and hepatobiliary safety.
Selected References
-
Basaria S. et al. Safety, PK/PD, and body-composition effects of LGD-4033 in healthy men (21-day RCT). J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
-
Dalton J.T., Kearbey J.D., et al. Nonsteroidal SARMs: pharmacology and therapeutic prospects. J Med Chem; Endocr Rev.
-
Gao W., et al. SARMs in muscle and bone—preclinical efficacy and selectivity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther; JBMR.
-
Evans N.A., Hasenoehrl T. Androgens, erythropoiesis, and cardiovascular risk. Hematology; Circulation Research.
-
Drug Testing & Analysis / WADA Lab Reports. LGD-4033 long-term metabolites and detection windows.
-
Case reports/series of SARM-associated liver injury in real-world use. Hepatology Communications; J Clin Transl Hepatol.