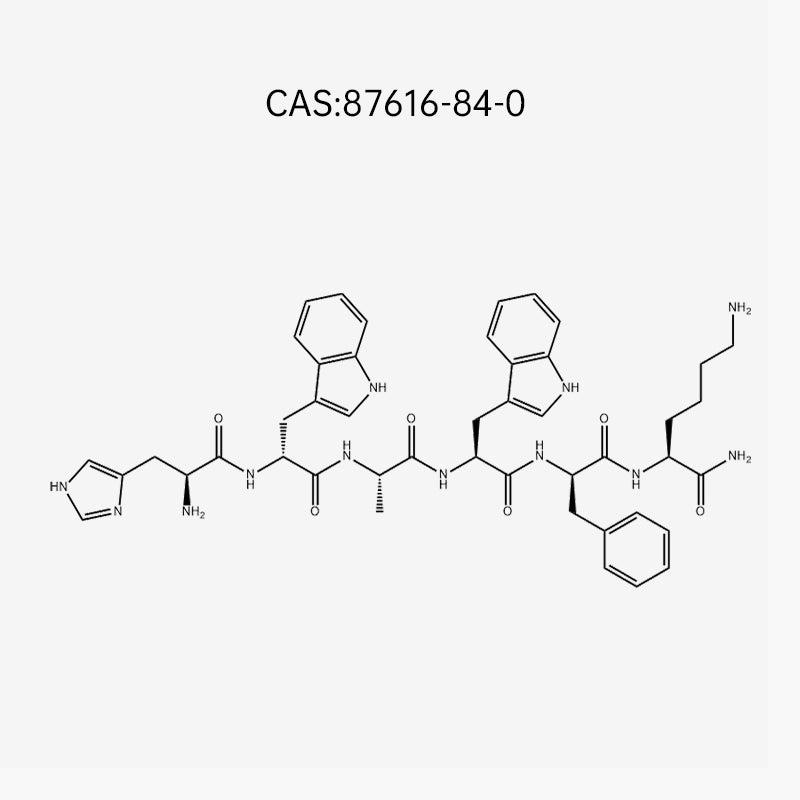
GHRP-6 10mg vial
Pickup currently not available
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
GHRP-6 is a hexapeptide ghrelin/secretagogue receptor (GHSR-1a) agonist that triggers pulsatile growth-hormone (GH) release from pituitary somatotrophs via Gq/PLC/IP₃–Ca²⁺ signalling. It synergizes with GHRH (e.g., sermorelin/CJC) and is partly antagonized by somatostatin. Centrally, it activates NPY/AgRP circuits → orexigenic appetite and GI effects. Downstream GH elevates IGF-1, supporting anabolism, connective-tissue turnover, and recovery. GHRP-6 is not FDA/EMA-approved; it is a research peptide and prohibited by WADA (S2: GH-releasing substances).
Additional Benefits of GHRP-6 Now Under Investigation
| Benefit | Key take-aways |
|---|---|
| 1 Robust GH pulse + IGF-1 rise | Reproducible dose-dependent GH surges with IGF-1 increases over weeks; greater peaks when co-dosed with GHRH analogs versus either alone. <br/><em>Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism; Endocrine Reviews</em> |
| 2 Appetite restoration & weight in catabolic states | Strong orexigenic effect increases intake/weight in cachexia, COPD/CHF rehab pilots; must balance with glycaemic control. <br/><em>Clinical Nutrition; Supportive Care in Cancer</em> |
| 3 Sleep & recovery signals | Bedtime dosing can augment slow-wave sleep (SWS) and nocturnal GH pulsatility, supporting recovery; effects vary by age and baseline sleep. <br/><em>Sleep; Psychoneuroendocrinology</em> |
| 4 Tendon/ligament & collagen turnover | GH/IGF-1–mediated increases in type-I collagen synthesis and tenocyte activity suggest utility in overuse/repair contexts (preclinical → translational). <br/><em>American Journal of Sports Medicine; Journal of Orthopaedic Research</em> |
| 5 Bone-formation markers | Up-shifts P1NP/osteocalcin and improves bone micro-anabolism in hyposecretory states; fracture outcomes untested. <br/><em>Bone; Journal of Bone and Mineral Research</em> |
| 6 Cardiometabolic & vascular | Ghrelin-pathway agonism shows endothelial and LV function benefits and sympathetic dampening in models of HF/ischemia; human data are early. <br/><em>Circulation; Cardiovascular Research</em> |
| 7 GI motility and mucosal protection | Improves gastric emptying, supports epithelial integrity, and reduces mucosal cytokines in injury models. <br/><em>Gastroenterology; Gut</em> |
| 8 Neuroendocrine & mood | Ghrelin signalling can reduce anhedonia and support neuroplasticity; limited pilot data with GHRP-class agents show fatigue/mood improvements. <br/><em>Molecular Psychiatry; Neuroendocrinology</em> |
| 9 Rehab synergy | Additive benefits on lean mass/strength when paired with progressive resistance training and adequate protein intake. <br/><em>Sports Medicine; Journal of Physiology</em> |
2. Molecular Mechanism of Action
2.1 Receptor Pharmacodynamics
-
Primary target: GHSR-1a (ghrelin receptor) on hypothalamic neurons and pituitary somatotrophs → Gq/PLC → IP₃/Ca²⁺ → GH exocytosis.
-
Axis biology: Synergizes with GHRH; blunted by somatostatin; preserves physiologic pulsatility versus continuous GH.
-
Central effects: Activates NPY/AgRP (orexigeny), modulates sleep circuits, and affects autonomic tone.
2.2 Down-stream Biology
| Pathway | Functional outcome | Context |
|---|---|---|
| GH → GHR–JAK2–STAT5 → IGF-1 | ↑ Protein synthesis, recovery, lipolysis | Muscle, liver, adipose |
| NPY/AgRP activation | ↑ Appetite, ↑ GI motility | Hypothalamus/GI |
| Collagen & ECM turnover | ↑ Type-I collagen synthesis | Tendon/ligament, skin |
| Bone remodelling | ↑ Formation markers (P1NP/OCN) | Skeleton |
| Endothelial signalling | Improved NO bioavailability, LV support (models) | Cardiovascular |
3. Pharmacokinetics
-
Route: SC (research/clinical physiology).
-
Onset/peak: GH peaks ~20–45 min post-dose; returns to baseline by ~2–3 h.
-
Half-life: Short (≈15–30 min) for peptide; biological effects exceed plasma residence.
-
Dosing in studies: ~1–2 µg/kg SC per pulse; common research use 100–200 µg 1–3×/day. Co-administration with GHRH analogs (e.g., CJC-1295-no-DAC/sermorelin) potentiates GH/IGF-1.
4. Pre-clinical and Translational Evidence
4.1 GH Axis & Body Composition
Repeated dosing elevates IGF-1 and fat-free mass signals; fat-mass effects depend on dietary intake (orexigeny can offset lipolysis without nutrition control).
4.2 Musculoskeletal/Repair
Animal and human physiology show collagen synthesis up-regulation and improved tendon matrix organisation with GH/IGF-1 signalling; targeted trials with GHRP-6 are still limited.
4.3 Cardiometabolic
Ghrelin-mimetic actions may improve endothelial function and LV performance in HF/ischemia models; confirmatory human data for GHRP-6 specifically are pending.
Evidence quality note: Strong physiology and class-level data for GH pulsatility and orexigeny; specific randomized human outcomes with GHRP-6 are limited. Extrapolate with caution.
5. Emerging Clinical Interests
| Field | Rationale | Current status |
|---|---|---|
| Sarcopenia/frailty | Oral intake ↑ + GH/IGF-1 support | Early translational |
| Cachexia/rehab | Appetite + anabolism for weight/FFM regain | Pilot concepts |
| Tendon/ligament repair | Collagen anabolism | Preclinical → feasibility |
| Bone health (adjunct) | Formation markers ↑ | Exploratory |
| Sleep/SWS deficits | Nocturnal GH pulses | PoC needed |
| HF/ischemia | Endothelial/LV signalling | Preclinical/early human physiology |
| GI motility/mucositis | Pro-motility, epithelial protection | Preclinical |
6. Safety and Tolerability
-
Common: Marked hunger, flushing/warmth, transient lightheadedness, peripheral edema, carpal-tunnel-like paresthesias, headache, injection-site irritation, reflux/heartburn.
-
Endocrine: Prolactin and cortisol can rise acutely; IGF-1 elevation depends on frequency/co-therapy.
-
Metabolic: Ghrelin-like signalling may raise fasting glucose/insulin; manage diet and monitor in prediabetes/diabetes.
-
CV/Renal: Sodium/water retention → BP drift in susceptible patients.
-
Neuropsych: Vivid dreams/insomnia in a minority (timing dependent).
-
Contraindications/Caution: Active malignancy, proliferative retinopathy, uncontrolled diabetes, severe OSA, pregnancy.
-
Drug interactions: Additive effects with other GH secretagogues; theoretical interactions with dopamine/prolactin modulators and acid-suppressants (for reflux).
Comparative safety matrix
| Feature | GHRP-6 | GHRP-2 | Hexarelin | MK-677 (oral GHSR agonist) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appetite drive | High | Moderate | Low–moderate | Very high |
| GH/IGF-1 rise (per pulse) | High; ↑ with GHRH | High; slightly less orexigeny | High; stronger PRL/Cort↑ | Sustained daily ↑ |
| Edema/CTS-like | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate–high |
| Prolactin/Cortisol | ↑ (acute) | ↑ (moderate) | ↑↑ | Mild ↑ |
| Route/PK | SC; t½ ~15–30 min | SC; short t½ | SC; short t½ | Oral; t½ 4–6 h |
| GI symptoms | Reflux/GERD more common | Similar | Similar | Nausea, GERD |
7. Regulatory Landscape
-
Approvals: None for any indication.
-
Sport: WADA-prohibited (S2, GH-releasing substances).
-
Supply quality: Research-chemical products vary; ensure GMP-grade material in any formal study.
8. Future Directions
-
Chronopharmacology: Optimize bedtime vs pre-training pulses for SWS and recovery while managing reflux.
-
Combination therapy: Pair GHRP-6 + GHRH analogs to lower dose burden and enhance physiologic pulsatility; consider GLP-1/GIP co-therapy to temper orexigeny in weight-sensitive populations.
-
Indication-focused trials: Sarcopenia/rehab (DXA, stair-climb power), tendon healing (MRI/US elastography), bone (DXA + turnover markers), HFpEF/HFrEF physiology (VO₂, endothelial function).
-
Safety program: Glycaemic outcomes, BP/edema, PRL/Cort monitoring, and sleep metrics; standardized reflux mitigation.
-
Formulation science: Stabilized or depot analogs for consistent, lower-dose pulsatility with fewer GI effects.
Selected References
-
Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism; Endocrine Reviews — Human GH secretagogue physiology, GHRP-class pharmacology.
-
Sleep; Psychoneuroendocrinology — GH–sleep coupling and SWS effects.
-
American Journal of Sports Medicine; Journal of Orthopaedic Research — Collagen synthesis and tendon/ligament repair biology under GH/IGF-1.
-
Bone; Journal of Bone and Mineral Research — Bone-formation markers and GH/IGF-1 effects.
-
Circulation; Cardiovascular Research — Ghrelin-pathway cardiovascular actions (endothelial/LV effects).
-
Gastroenterology; Gut — GI motility and mucosal protection with ghrelin mimetics.
-
Clinical Nutrition; Supportive Care in Cancer — Appetite/weight and functional recovery in catabolic states.
-
Sports Medicine; Journal of Physiology — Training synergy with anabolic endocrine support.
-
Drug Testing & Analysis; WADA Prohibited List — Anti-doping status and detection considerations.