BPC-157 pellets 100x500mcg
Pickup currently not available
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
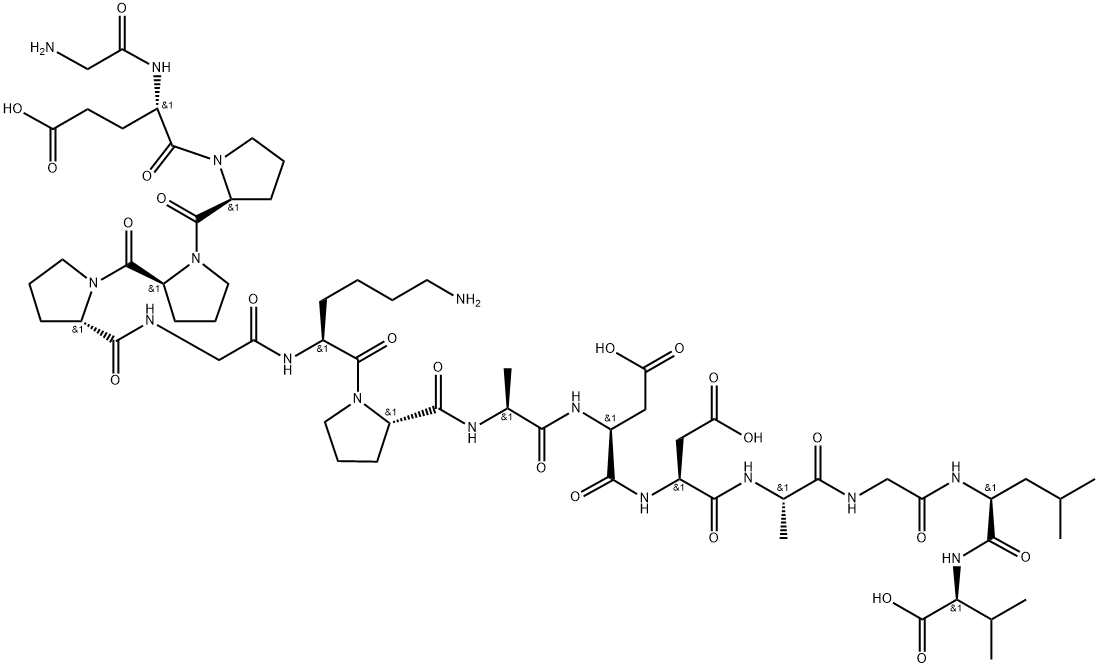
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound 157) is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a protein in human gastric juice. Discovered in the 1990s, it has attracted significant interest for its potential regenerative, protective, and healing properties, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal system, and nervous system.
Chemical and Pharmacological Background
-
Full Name: Body Protection Compound-157
-
Structure: Synthetic peptide comprising 15 amino acids (Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val)
-
Origin: Derived from a protective protein sequence naturally found in human gastric juice
-
Administration Route: Subcutaneous injection, intramuscular injection, oral administration (less bioavailable), topical application (experimental)
Mechanisms of Action
BPC-157’s proposed mechanisms are multifaceted and complex, involving various physiological pathways:
1. Angiogenesis and Blood Vessel Formation
-
Significantly enhances angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, facilitating improved nutrient delivery and tissue healing.
2. Enhanced Cellular Survival and Tissue Repair
-
Upregulates growth factors and receptors associated with cellular regeneration.
-
Facilitates healing and recovery in musculoskeletal tissues (tendons, ligaments, muscles).
3. Anti-Inflammatory and Cytoprotective Actions
-
Potently reduces inflammation and oxidative stress in various tissues.
-
Protects cells and tissues from toxic insults, injury, and oxidative damage.
4. Modulation of Nitric Oxide (NO) Pathways
-
Regulates NO synthesis, thereby affecting vascular tone, inflammation, and wound healing processes.
5. Neuroprotection and Neurogenesis
-
Potentially exerts protective effects on neurons, possibly promoting neural regeneration and neurogenesis after injury.
6. Gastrointestinal Protection and Healing
-
Demonstrates significant protective and healing effects in gastrointestinal mucosa, beneficial in treating ulcers, inflammation, and damage.
Potential Therapeutic Applications
BPC-157 has been researched and discussed in contexts ranging from injury repair to chronic inflammatory conditions:
1. Musculoskeletal Injuries
-
Accelerates healing of tendons, ligaments, muscles, and bones.
-
Demonstrated improvements in tendon healing (Achilles tendon, patellar tendon injuries).
2. Gastrointestinal Disorders
-
Effective in healing gastric ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and intestinal injury.
-
Reduces gut inflammation, promotes intestinal integrity, and improves gastrointestinal function.
3. Inflammatory and Autoimmune Conditions
-
Potential benefit for arthritis and inflammatory conditions due to anti-inflammatory actions.
4. Neurodegenerative and Neurological Injuries
-
Possible neuroprotective effects following brain injuries, stroke, peripheral nerve injury, and spinal cord injury.
5. Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration
-
Accelerates healing of skin wounds, burns, surgical incisions, and diabetic ulcers.
Dosage and Administration (Experimental / Anecdotal)
No officially approved dosing guidelines exist, as human clinical studies are limited. However, commonly reported experimental dosages include:
-
Subcutaneous / Intramuscular Injection:
-
Common Dosage Range: 250–500 mcg daily (occasionally up to 1 mg daily).
-
Typically administered as single or divided doses near injury sites or systemically.
-
-
Oral Administration (Experimental & Less Bioavailable):
-
Oral doses range widely (e.g., 250–1000 mcg/day) but are considered less effective due to peptide degradation in the digestive tract.
-
-
Cycle Duration:
-
Generally used experimentally for 2–6 weeks, followed by breaks or evaluations of effects.
-
Note: Dosages cited here reflect anecdotal user reports and limited clinical trials; safety and efficacy have not been definitively established by robust human trials.
Safety Profile and Side Effects
Preclinical animal studies and anecdotal human reports suggest a favorable safety profile:
Commonly Reported Side Effects:
-
Minimal side effects, generally well-tolerated at typical dosages.
-
Rare mild irritation at injection site, transient discomfort, mild dizziness (rare).
Long-Term Safety and Risks:
-
Unknown due to limited human clinical research.
-
Further controlled clinical studies needed to establish definitive safety profile.
Dependence and Withdrawal Risks:
-
No current evidence of tolerance, dependence, or withdrawal issues.
Contraindications and Drug Interactions
Contraindications:
-
Hypersensitivity to peptide compounds.
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding (lack of safety data; avoidance advised).
Interactions:
-
No confirmed significant drug interactions known.
-
As BPC-157 affects blood vessel formation and inflammatory pathways, caution is advised when combined with anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory medications, or immunosuppressants.
Legal and Regulatory Status
-
FDA and International Regulatory Status: Not currently approved by FDA, EMA, Health Canada, or other major regulatory bodies for therapeutic use in humans.
-
Typically sold as a research chemical or experimental peptide, labeled "not for human consumption."
-
Legal status varies by country; unregulated status requires careful sourcing due to potential purity and authenticity concerns.
Current Research Status
Preclinical Research:
-
Numerous animal studies demonstrate robust healing effects on gastrointestinal tissues, tendon healing, wound healing, inflammation, and nerve repair.
-
Notable evidence for tissue regeneration and cytoprotection.
Human Clinical Trials:
-
Currently limited and primarily anecdotal or small-scale studies.
-
Ongoing clinical trials listed occasionally (check ClinicalTrials.gov for updates).
Limitations and Needs for Future Research:
-
Significant lack of large-scale, placebo-controlled human clinical studies.
-
Need for clearly defined dosing protocols, long-term safety assessments, and comprehensive efficacy evaluation.
Summary of Potential Benefits and Risks
| Potential Benefits | Possible Risks and Limitations |
|---|---|
| Enhanced healing of tendons, ligaments, muscles, bones | Limited long-term human safety data |
| Gastrointestinal healing and anti-inflammatory actions | Unclear regulatory status globally |
| Neuroprotective and nerve regeneration potential | Limited human clinical evidence |
| Favorable short-term safety and minimal side effects | Peptide stability and bioavailability issues orally |
| Broad spectrum of regenerative therapeutic applications | Need for standardized and validated dosing protocols |
References
-
Seiwerth, S., et al. (2014). "BPC 157 and blood vessels." Current Pharmaceutical Design, 20(7), 1121–1125.
-
Sikirić, P., et al. (2020). "Stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157: novel therapy in gastrointestinal tract." Current Pharmaceutical Design, 26(25), 2991–3001.
-
Gwyer, D., et al. (2019). "BPC 157 as a potential therapy for tendon injuries." Muscles, Ligaments and Tendons Journal, 9(2), 189–192