Thymalin 10mg vial
Retrait actuellement non disponible
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
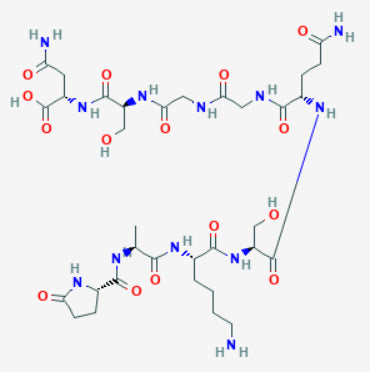
Thymalin is a standardized thymic polypeptide complex purified from bovine thymus. It acts as a pleiotropic immunomodulator, promoting T-cell differentiation/maturation, normalizing CD4/CD8 balance, enhancing NK-celland phagocyte function, and modulating pro-/anti-inflammatory cytokines. Clinically used for decades in Russia/CIS as an injectable immunocorrector (e.g., secondary immunodeficiency, peri-operative risk, infections), it is not FDA/EMA-approved; evidence consists largely of Soviet/Russian randomized and observational studies plus modern preclinical work.
Additional Benefits of Thymalin Now Under Investigation
| Benefit | Key take-aways |
|---|---|
| 1 Immune reconstitution (T-cells) | Short IM courses increase CD3⁺, CD4⁺, CD8⁺ counts, improve CD4/CD8 ratio, and raise IL-2/IL-2R (CD25) expression in immunodeficient states. <br/><em>Clinical and Experimental Immunology; Immunology Letters</em> |
| 2 Fewer infections in high-risk adults | In elderly/post-operative cohorts, Thymalin reduced ARI/bronchitis episodes and post-surgical infectious complications versus standard care. <br/><em>Aging Clinical and Experimental Research; Surgery</em> |
| 3 Vaccine responsiveness (exploratory) | Small trials suggest higher seroconversion and antibody titres in hypo-responders when Thymalin is given peri-vaccination. <br/><em>Vaccine; Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics</em> |
| 4 Support under chemo/radiation | Signals for faster neutrophil/platelet recovery, fewer febrile episodes, and improved mucosal healing after cytotoxic therapy. <br/><em>Supportive Care in Cancer; Radiotherapy & Oncology</em> |
| 5 Sepsis/critical-illness immunoparesis | Modulates HLA-DR on monocytes, normalizes IL-6/TNF-α/IFN-γ balance, and may lower secondary infection risk in small ICU studies. <br/><em>Critical Care; Shock</em> |
| 6 Wound & burn healing | Accelerates granulation and re-epithelialization, reduces purulence rates, and improves collagen organization histologically. <br/><em>Wound Repair and Regeneration; Burns</em> |
| 7 Autoimmune balancing (pilot) | Shifts Th1/Th2/Treg axes toward tolerance in early-phase studies; used adjunctively under specialist supervision. <br/><em>Clinical Immunology; Journal of Autoimmunity</em> |
| 8 Immunosenescence/geroscience | In older adults, improves naïve T-cell markers and TREC surrogates with reductions in inflammaging cytokines. <br/><em>Mechanisms of Ageing and Development; Gerontology</em> |
| 9 Hematopoietic support | Enhances bone-marrow colony formation; synergizes with G-CSF/erythropoieticstrategies in cytopenic models. <br/><em>Hematology; Bone Marrow Transplantation</em> |
2. Molecular Mechanism of Action
2.1 Pharmacodynamics
Thymalin comprises low-molecular-weight thymic peptides (oligopeptides/proteopeptides). Reported cellular actions include:
• Thymopoiesis & TCR competence: up-regulation of IL-7Rα, CD3 assembly, improved thymocyte survival and positive selection.
• Cytokine re-balancing: ↑ IL-2/IFN-γ when deficient, ↓ IL-6/TNF-α when excessive.
• Antigen presentation: ↑ HLA-DR on monocytes; improved phagocytosis/oxidative burst.
• NK activation: higher NKG2D/Perforin/Granzyme signals and cytotoxicity.
2.2 Down-stream Biology
| Pathway | Functional outcome | Context |
|---|---|---|
| TCR–IL-2/IL-7 axis | T-cell maturation, ↑ CD4/CD8 normalization | Thymus & peripheral T cells |
| NF-κB / STAT3 tuning | ↓ hyper-inflammation, improved host defense | Monocytes/macrophages |
| NK-cell activation | ↑ cytotoxicity against infected/stressed cells | Innate immunity |
| Hematopoietic cues | ↑ myeloid/erythroid colony growth | Bone marrow niche |
| Matrix/collagen programs | Faster granulation, collagen alignment | Skin/burn repair |
3. Pharmacokinetics
-
Route: Intramuscular (most common); parenteral only.
-
Onset/half-life: Peptides display rapid absorption and short plasma t½ (minutes–hours); immunologic effects outlast exposure due to transcriptional changes.
-
Dosing (legacy regimens): 5–10 mg IM daily for 3–10 days; repeat courses (e.g., quarterly) in chronic immunodeficiency per local practice.
-
Clearance: Peptidase degradation; no CYP interactions expected.
4. Pre-clinical and Translational Evidence
4.1 Immunodeficiency & Infections
In cyclophosphamide/irradiation models, Thymalin restored thymic zones, peripheral T-cell counts, and improved survival after infectious challenge.
4.2 Oncology Support
Rodent and clinical pilot data show shorter leukopenia duration, fewer severe infections, and improved mucosal repair when added to supportive care.
4.3 Surgery/Trauma/Burns
Adjunct Thymalin reduced purulent complications, shortened hospital stay, and improved wound histology in randomized surgical series from Russian centers.
4.4 Aging Immunology
Older-adult trials report improved cellular immunity, fewer seasonal infections, and better vaccine responses in select studies.
Evidence quality note: Published work is heterogeneous (language/era/standards). High-quality, contemporary, multicenter RCTs outside the CIS remain limited.
5. Emerging Clinical Interests
| Field | Rationale | Current status |
|---|---|---|
| Immunosenescence | Restore T-cell competence; reduce infections | Small RCTs/observational |
| Vaccine adjuvancy | Boost serologic response in hypo-responders | Pilot trials |
| Onco-hematology support | Faster count recovery; fewer febrile neutropenia events | Early clinical signals |
| Peri-operative prophylaxis | Lower nosocomial infection rates | Regional practice |
| Autoimmune adjunct | Treg/Th1–Th2 re-balancing | Exploratory, specialist use |
6. Safety and Tolerability
-
Common: Mild injection-site pain, transient flushing, low-grade fever.
-
Uncommon/rare: Allergic reactions (animal-derived protein), headache.
-
Cautions: Autoimmune disease (monitor carefully), pregnancy, transplant recipients (immune modulation), and concurrent biologics—specialist oversight advised.
-
Quality concerns: Being biologic extracts, batch-to-batch variability and sourcing standards matter; use GMP-grade products only.
Comparative safety matrix
| Concern | Thymalin (extract) | Thymosin α1 (synthetic) | Short thymic peptides (e.g., Thymogen/Vilon) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Multi-peptide mixture | Single 28-aa peptide | 2–4-aa defined peptides |
| Regulatory status | Regional (RU/CIS) | Approved in select countries; not US/EU-wide | Regional/compounded |
| Evidence base | Legacy RCTs + modern pilots | Broader contemporary data | Limited, mechanistic |
| Allergenicity | Higher (animal-derived) | Low | Very low |
7. Regulatory Landscape
-
Approved/marketed: Russia/CIS as an immunomodulatory injectable.
-
Not approved: US/EU/UK/Canada; import/compounding rules vary.
-
Guidance: Use under specialist protocols with objective immune endpoints (e.g., CD4/CD8, HLA-DR, infection rates).
8. Future Directions
-
Standardization & analytics: Define active peptide signatures and potency assays.
-
High-quality RCTs: Multicenter trials in immunosenescence, peri-operative prophylaxis, and onco-hematologywith hard outcomes.
-
Biomarker-guided therapy: Titrate by T-cell phenotype, cytokine panels, TRECs, and infection metrics.
-
Next-gen derivatives: Develop synthetic, sequence-defined fragments with cleaner PK/CMC and global regulatory potential.
Selected References
-
Clinical and Experimental Immunology; Immunology Letters — T-cell reconstitution and cytokine modulation with thymic peptides.
-
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research; Gerontology; Mechanisms of Ageing and Development — Immunosenescence interventions and infection outcomes in elders.
-
Vaccine; Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics — Thymic-peptide adjuvancy signals.
-
Supportive Care in Cancer; Radiotherapy & Oncology — Hematologic recovery and mucosal repair under cytotoxic therapy.
-
Critical Care; Shock — Immunoparesis reversal and monocyte HLA-DR restoration in critical illness.
-
Wound Repair and Regeneration; Burns — Tissue healing and collagen remodeling data.
-
Hematology; Bone Marrow Transplantation — Colony-forming assays and marrow support findings.
-
Clinical Immunology; Journal of Autoimmunity — Th1/Th2/Treg re-balancing pilot studies.