MOTS-c 10mg vial
Vyzvednutí není momentálně k dispozici
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
MOTS-c is a recently discovered mitochondrial-derived peptide encoded by mitochondrial DNA. Identified in 2015, MOTS-c plays a significant role in regulating metabolism, energy homeostasis, mitochondrial function, insulin sensitivity, and potentially longevity. Due to its unique mitochondrial origin and metabolic-regulatory properties, MOTS-c has attracted interest as a potential therapeutic agent in metabolic and aging-related disorders.
Chemical and Biological Properties
-
Full Name: Mitochondrial Open Reading Frame of the Twelve S rRNA type-c
-
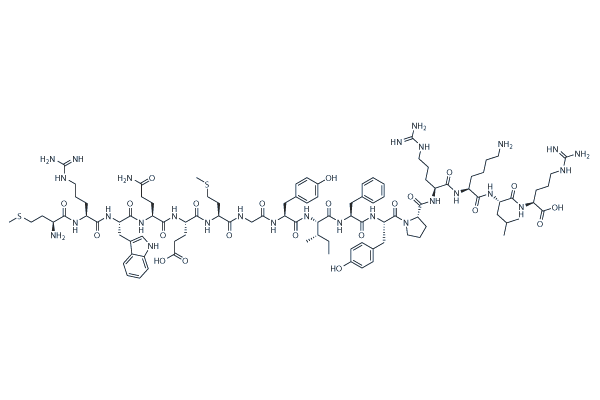
Structure: Small peptide (16 amino acids: MRWQEMGYIFYPRKLR)
-
Origin: Encoded by mitochondrial DNA, synthesized and released into the cytoplasm and systemic circulation
-
Administration Routes: Typically administered via subcutaneous injection in experimental studies due to peptide stability and bioavailability considerations
Mechanism of Action
MOTS-c acts primarily through metabolic modulation and mitochondrial regulation:
1. Metabolic Regulation and Insulin Sensitivity
-
Activates the AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) pathway, a critical regulator of energy homeostasis, glucose metabolism, and fatty acid oxidation.
-
Improves insulin sensitivity, glucose uptake, and overall metabolic health.
2. Enhancement of Mitochondrial Function and Biogenesis
-
Increases mitochondrial biogenesis and efficiency, enhancing cellular energy production.
-
May protect against metabolic disorders and aging-related declines in mitochondrial function.
3. Anti-inflammatory and Cytoprotective Effects
-
Reduces inflammation and oxidative stress, potentially protecting tissues from chronic metabolic stress.
4. Exercise Mimetic ("Exercise in a Pill")
-
MOTS-c mimics some beneficial effects of exercise, potentially improving endurance, performance, and metabolic health without physical activity.
Potential Therapeutic and Experimental Applications
MOTS-c has shown promising potential in several preclinical and experimental contexts:
1. Type 2 Diabetes and Insulin Resistance
-
Demonstrates significant improvements in glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity, potentially beneficial for managing type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
2. Obesity and Weight Management
-
Enhances fatty acid oxidation, energy expenditure, and metabolism, potentially aiding in weight loss or obesity prevention.
3. Longevity and Healthy Aging
-
Proposed as a novel longevity-promoting compound due to mitochondrial protection, improved metabolism, and reduced inflammation.
-
May prevent age-related metabolic dysfunction, sarcopenia (muscle wasting), and cognitive decline.
4. Cardiovascular Health
-
Potentially beneficial for cardiovascular disease prevention due to anti-inflammatory, metabolic, and antioxidant properties.
5. Physical Performance and Endurance Enhancement
-
Preclinical studies suggest MOTS-c enhances physical endurance, exercise performance, and muscular efficiency, leading to interest as a performance-enhancing compound.
Dosage and Administration (Experimental Context)
No established clinical dosage guidelines exist due to limited human studies. Typical experimental dosages based on preclinical studies and anecdotal reports are:
-
Dosage Range: 5–15 mg per administration (common experimental doses: 5–10 mg weekly).
-
Route of Administration: Subcutaneous injection, typically once weekly.
-
Experimental Cycle Length: Usually administered experimentally over 4–8 weeks, followed by an evaluation period.
Note: The above dosages are experimental and not clinically validated; human equivalent dosages require rigorous clinical research.
Safety Profile and Side Effects
Due to the limited clinical human trials, full safety profiles remain preliminary; however, preclinical studies suggest favorable tolerability:
Common Side Effects (Rare and Mildly Reported):
-
Mild injection-site discomfort, redness, or swelling.
-
Transient dizziness, mild fatigue, or headaches (rarely reported).
Long-term Safety and Risks:
-
Insufficient long-term safety data available.
-
No reported evidence of dependency, addiction, or withdrawal symptoms in existing studies.
Contraindications and Precautions
-
Contraindications:
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding (unknown safety profile).
-
Known hypersensitivity to peptide-based compounds.
-
-
Drug Interactions:
-
Limited known drug interactions; caution advised when used concurrently with insulin, oral hypoglycemics, or other metabolic modulators.
-
-
Precautions:
-
Patients with severe metabolic disorders or insulin-dependent diabetes should consult healthcare professionals due to MOTS-c’s potent metabolic effects.
-
Legal and Regulatory Status
-
Approval and Regulation: MOTS-c is currently not approved by major regulatory agencies (FDA, EMA, Health Canada) for therapeutic human use.
-
Typically available as a "research peptide" or experimental compound labeled as "not for human consumption."
-
Not explicitly banned by WADA; athletes should confirm updated regulations before competitive use.
Current Research Status and Evidence
-
Preclinical Research:
-
Numerous animal studies demonstrate significant metabolic improvements, endurance enhancement, longevity-related effects, and mitochondrial protective benefits.
-
-
Human Clinical Trials:
-
Very limited, with initial exploratory studies ongoing or in planning stages.
-
Preliminary small-scale observational studies and anecdotal evidence suggest metabolic benefits and improved exercise tolerance, though larger controlled trials are necessary.
-
-
Research Limitations and Future Directions:
-
Lack of extensive human clinical data and randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
-
Need for standardized dosing, long-term safety evaluation, and clearly defined clinical efficacy.
-
Summary of Potential Benefits and Risks
| Potential Benefits | Potential Risks and Limitations |
|---|---|
| Improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic health | Limited human clinical data |
| Potential longevity and anti-aging effects | Unclear long-term safety profile |
| Enhanced exercise performance and endurance | Possible interactions with metabolic medications |
| Anti-inflammatory and mitochondrial protective effects | Regulatory uncertainty; experimental availability |
Future Directions and Research Needs
-
Conduct rigorous human clinical trials to establish efficacy, safety, optimal dosing, and therapeutic potential.
-
Long-term studies needed to evaluate potential chronic effects, safety, and effectiveness in various populations.
-
Exploration of MOTS-c’s therapeutic potential in metabolic diseases, aging, cardiovascular diseases, and physical performance enhancement.
Conclusion
MOTS-c is a promising mitochondrial-derived peptide with demonstrated metabolic, mitochondrial, and potential anti-aging benefits. Preclinical research strongly supports its potential role in managing metabolic disorders, promoting healthy aging, and enhancing exercise performance. However, significant gaps in clinical research, dosing standardization, and long-term safety evaluations remain. Until comprehensive human studies confirm safety and efficacy, MOTS-c remains a novel experimental compound with substantial therapeutic promise.
References
-
Lee, C., et al. (2015). "The mitochondrial-derived peptide MOTS-c promotes metabolic homeostasis and reduces obesity and insulin resistance." Cell Metabolism, 21(3), 443–454.
-
Kim, K. H., & Son, J. M. (2019). "Mitochondrial peptides as promising targets for age-related metabolic disorders." Experimental Gerontology, 121, 15–19.
-
Reynolds, J. C., et al. (2021). "MOTS-c is an exercise-induced mitochondrial-encoded regulator of age-dependent physical decline and muscle homeostasis." Nature Communications, 12(1), 470.
Disclaimer:
This product is provided exclusively for educational purposes. MOTS-c is an experimental research compound and has not been approved by major health regulatory authorities for clinical therapeutic use. Always consult qualified healthcare providers before considering experimental peptides or supplements.